Unearned Revenues
Unearned revenues are payments for future services
to be performed or goods to be delivered. Advance customer payments for
newspaper subscriptions or extended warranties are unearned revenues at
the time of sale. At the end of each accounting period, adjusting
entries must be made to recognize the portion of unearned revenues that
have been earned during the period.
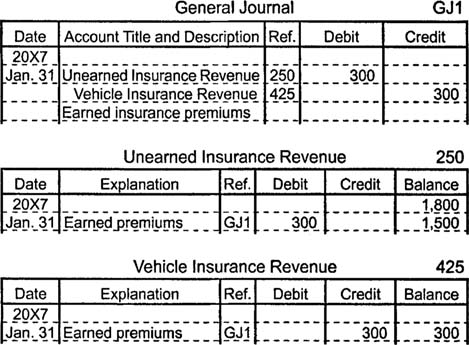
Suppose a customer pays $1,800 for an insurance policy to protect
her delivery vehicles for six months. Initially, the insurance company
records this transaction by increasing an asset account (cash) with a
debit and by increasing a liability account (unearned revenue) with a
credit. After one month, the insurance company makes an adjusting entry
to decrease (debit) unearned revenue and to increase (credit) revenue by
an amount equal to one sixth of the initial payment.
Accounting records that do not include adjusting entries to show
the earning of previously unearned revenues overstate total liabilities
and understate total
Prepaid Expenses
Prepaid expenses are assets that become expenses as
they expire or get used up. For example, office supplies are considered
an asset until they are used in the course of doing business, at which
time they become an expense. At the end of each accounting period,
adjusting entries are necessary to recognize the portion of prepaid
expenses that have become actual expenses through use or the passage of
time.
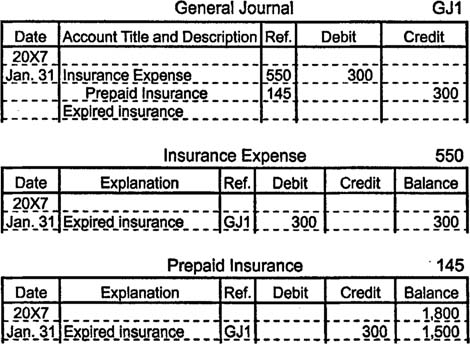
Consider the previous example from the point of view of the
customer who pays $1,800 for six months of insurance coverage.
Initially, she records the transaction by increasing one asset account
(prepaid insurance) with a debit and by decreasing another asset account
(cash) with a credit. After one month, she makes an adjusting entry to
increase (debit) insurance expense for $300 and to decrease (credit)
prepaid insurance for $300.
Prepaid expenses in one company's accounting records are often—but
not always—unearned revenues in another company's accounting records.
Office supplies provide an example of a prepaid expense that does not
appear on another company's books as unearned revenue.
Accounting records that do not include adjusting entries to show
the expiration or consumption of prepaid expenses overstate assets and
net income and understate expenses.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar